Implementation > Consulting > Groundwater and artificial groundwater surveys
Well location surveys including deep research methods
Soil sample gathering is inconvenient in eskers where soil types change radically both in horizontal and in vertical direction. We use precise systems to measure hydraulic conductivity in all of the layers in the screened area of observation well. Patented measurement system can be used to measure hydraulic conductivity and location of the best layers with great accuracy. Well dimensioning can be determined reliably before construction. In turnkey-projects we offer a warranty for the yield of the well.
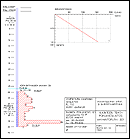
Hydraulic conductivity measurements at Vuonteenharju from an observation well.
Test pumping from a test well
Yield and quality of groundwater is measured reliably by conducting a long-term test pumping. Test pumping is conducted by drilling wells that are used to pump groundwater. The amount and positioning of test wells depends on the required yield and aquifer properties. Usually test wells are constructed into central parts of an esker where the hydraulic conductance and water quality is typically good. If the test well is positioned and constructed professionally, it can be used for the main well of the new waterworks.

Test well and test pumping at Virttaangangas, Turku.
Real-time measurements of groundwater level quality
During test pumping and test recharge, groundwater level, pumped quantities and water quality are monitored closely and frequently. Using real-time measurement systems enables us to establish a precise modeling dataset and saves manpower.
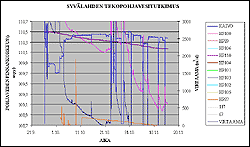
Real time measurements of groundwater level and water flow rates at Sumiainen.
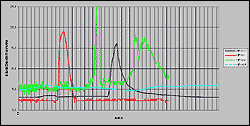
Groundwater quality at Jyväskylä.
Ground water flow velocity and direction measurements
Groundwater flow direction and velocity have a high impact on artificial groundwater cleansing and groundwater contamination. When groundwater direction and velocity can be measured, a risk management plan can be devised.
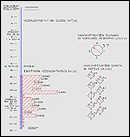
Hydraulic conductivity of soil and groundwater flow velocity and direction.

Measurement of groundwater flow at Rusutjärvi.
Groundwater flow and aquifer modeling
Artificial groundwater surveys are usually accompanied with models. Groundwater modeling in the case of artificial recharge means representing the physical phenomenon of hydraulic flow. This is always done by computer aided calculation.
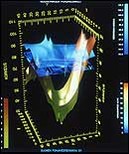
Artificial recharge model of Muuratharju aquifer.
In the calibration stage, all of the parameters are defined for the model. The model should act as closely as possible like the real aquifer being modeled. The model is used to calculate groundwater levels and water balances which are then compared to the measured values. In different pumping and recharge cases the modeled values should correspond the measured values.
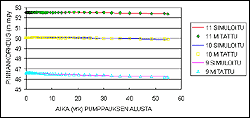
Groundwater model calibration results of Säpilänniemi aquifer.
Functioning of the planned artificial groundwaterworks is simulated with the groundwater model. Simulations are used to estimate the effects of pumping and recharging or groundwater and to optimize the operation of the waterworks. Groundwater contours, springs, dilution and dwell time can be printed from a simulation. The environmental effects of artificial groundwater are caused by both construction and groundwater level change. This can be seen in spring levels, in river flow and discharge. The change in groundwater level can also prevent the pumping from a private owned well. This can be prevented by carefully planning the artificial groundwater project.
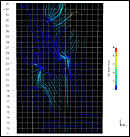
Simulation of water particle movement at Vuonteenharju, Jyväskylä.
Artificial groundwater quality is influenced by geology, position and amount of recharge and pumping as well as the untreated water. The purifying of the untreated water is a complex process. One of the most important factors influencing the process is the dwell time. Dwell time can be determined from a groundwater model that has been calibrated by measurements at the aquifer without tracer tests. This allows precise positioning of recharge and pumping areas and quality predictions.
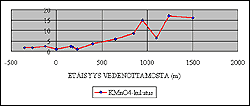
Artificial groundwater quality at Ahvenisto, Hämeenlinna.
Patents and methods
Hydraulic conductivity measurements are conducted using a patented method which allows precise measurements of each soil layer regardless of the hydraulic pressure. Groundwater flow velocity and direction are measured using self-developed instruments. We have used real-time, self-developed, measurement systems in test pumping from 1987.


